
Molecular sieves and molecular sieve active powder are closely related, and they have the same chemical composition. It is a type of porous material commonly used for adsorption and separation processes in various industrial applications. It consists of tiny particles with a high surface area and intricate pore structure that allows them to selectively adsorb molecules based on their size and polarity.



The production of raw materials for molecular sieve active powder typically involves the synthesis of crystalline aluminosilicates or other metal oxide frameworks. This is often achieved through hydrothermal reactions where silica and alumina sources are combined with specific templates and alkaline solutions. These templates guide the formation of the desired pore structure. The resulting gel is then subjected to controlled heating and crystallization processes to create the porous framework. The raw material may be further processed by grinding and milling to produce the desired powder particle size. The exact synthesis conditions and precursors used can be adjusted to tailor the pore size, surface area, and adsorption properties of the molecular sieve active powder for various industrial applications.
High Surface Area: Molecular sieve powder exhibits a high surface area due to its porous structure, allowing for efficient adsorption of molecules.
Thermal and Chemical Stability: They exhibit excellent stability at elevated temperatures and in the presence of various chemicals, making them suitable for harsh industrial conditions.
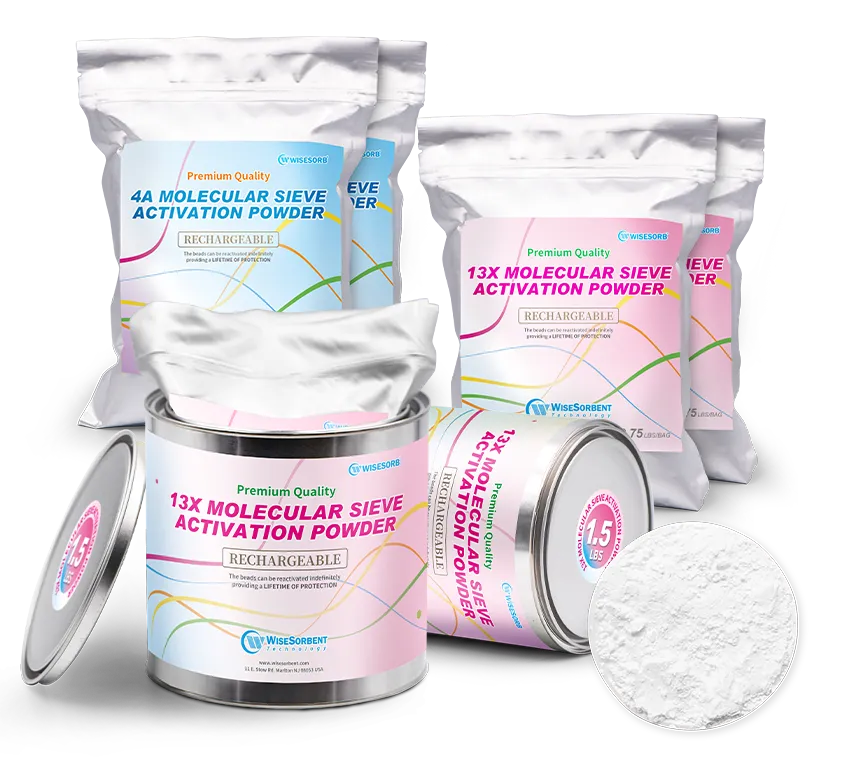

Molecular sieve activated powder possesses excellent dispersibility and extremely rapid adsorption speed. It can effectively remove unnecessary reaction water and other impurities from materials, suitable especially in industrial circumstances.

Polyurethane systems (coatings, paints, adhesives, etc.): Removing unnecessary reaction water from the system.
Hollow glass sealing strips: Eliminating water from coatings and sealing materials in the window manufacturing process.